Products
-
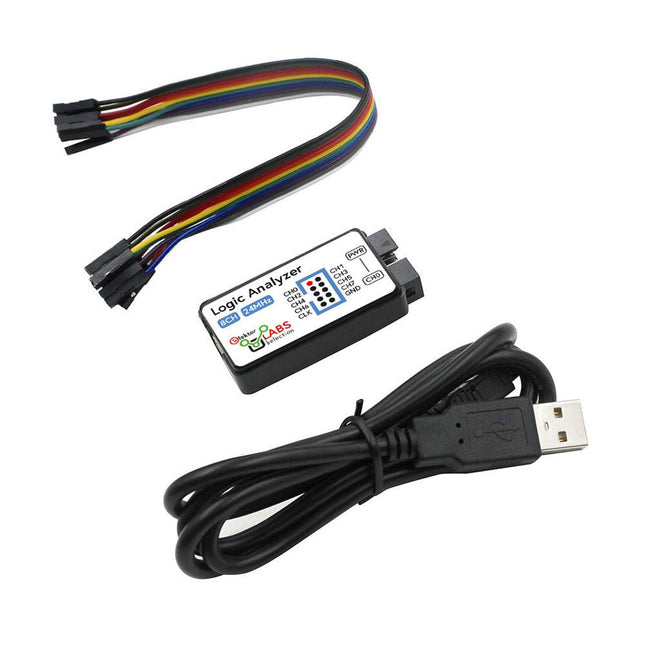

Elektor Labs USB Logic Analyzer (8-ch, 24 MHz)
This USB Logic Analyzer is an 8-channel logic analyzer with each input dual purposed for analog data recording. It is perfect for debugging and analyzing signals like I²C, UART, SPI, CAN and 1-Wire. It operates by sampling a digital input connected to a device under test (DUT) at a high sample rate. The connection to the PC is via USB. Specifications Channels 8 digital channels Maximum sampling rate 24 MHz Maximum input voltage 0~5 V Operating temperature 0~70°C Input impedance 1 MΩ || 10 pF Supported protocols I²C, SPI, UART, CAN, 1-Wire, etc. PC connection USB Dimensions 55 x 28 x 14 mm Included USB Logic Analyzer (8-ch, 24 MHz) USB Cable Jumper Wire Ribbon Cable Downloads Software
€ 14,95
Members € 13,46
-

Elektor Digital Using Displays in Raspberry Pi Projects (E-book)
Learn to program displays and GUIs with Python This book is about Raspberry Pi 4 display projects. The book starts by explaining how to install the latest Raspbian operating system on an SD card, and how to configure and use the GPIO ports. The core of the book explains the following topics in simple terms with fully tested and working example projects: Simple LED projects Bar graph LED projects Matrix LED projects Bitmap LED projects LED strips LCDs OLED displays E-paper displays TFT displays 7-inch touch screen GUI Programming with Tkinder One unique feature of this book is that it covers almost all types of display that readers will need to use in their Raspberry Pi based projects. The operation of each project is fully given, including block diagrams, circuit diagrams, and commented full program listings. It is therefore an easy task to convert the given projects to run on other popular platforms, such as Arduino or PIC microcontrollers. Python program listings of all Raspberry Pi projects developed in this book are available for download at Elektor.com. Readers can use these programs in their projects. Alternatively, they can modify the programs to suit their applications.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Elektor Digital Vanderveen Trans Tube Amplifiers (E-book)
Menno van der Veen is well known for his research publications on tube amplifiers used in audio systems. In this book he describes one of his research projects which focuses on the question of whether full compensation for distortion in tubes and output transformers is possible. In the past, a variety of techniques have been developed. One of them has largely been forgotten: trans-conductance, which means converting current into voltage or voltage into current. Menno van der Veen has breathed new life into this technique with his research project titled “Trans”. This book discusses all aspects of this method and discusses its pitfalls. These pitfalls are addressed one by one. The end result is a set of stringent requirements for Trans amplifiers. Armed with these requirements, Menno then develops new Trans amplifiers, starting with Transie 1 and Transie 2. These DC-coupled, single-ended tube amplifiers have unusually good characteristics and are suitable for hobbyist construction. Next the Trans principle is applied to amplifiers with higher output power. A trial-and-error process ultimately leads to the Vanderveen Trans 30 amplifier, which optimizes the features of Trans. The characteristics of this amplifier are so special and unique that Menno believes he has struck gold. To ensure that variations in tube characteristics cannot interfere with optimal Trans behavior, Menno makes use of simulations and comparison with other amplifier types. This book reads like an adventure story, but it is much more – it is an account of solid research into new ways to achieve optimal audio reproduction.
€ 29,95
Members € 23,96
-

Elektor Publishing Vintage Radio Equipment
Resonances From Aether Days A Pictorial and Technical Analysis from WWII to the Internet Age From the birth of radio to the late 1980s, much of real life unfolded through shortwave communication. World War II demonstrated—beyond a shadow of a doubt—that effective communications equipment was a vital prerequisite for military success. In the postwar years, shortwave became the backbone on which many of the world's most critical services depended every day. All the radio equipment—through whose cathodes, grids, plates, and transistors so much of human history has flowed—is an exceptional subject of study and enjoyment for those of us who are passionate about vintage electronics. In this book, which begins in the aftermath of World War II, you’ll find a rich collection of information: descriptions, tips, technical notes, photos, and schematics that will be valuable for anyone interested in restoring—or simply learning about—these extraordinary witnesses to one of the most remarkable eras in technological history. My hope is that these pages will help preserve this vast treasure of knowledge, innovation, and history—a heritage that far transcends the purely technical.
€ 79,95
Members € 71,96
-

Elektor Digital Visual Basic for Electronics Engineering Applications (E-book)
The PC has long-time outgrown its function as a pure computer and has become an all-purpose machine. This book is targeted towards those people that want to control existing or self-built hardware from their computer. Using Visual Basic as Rapid Application Development tool we will take you on a journey to unlock the world beyond the connectors of the PC. After familiarising yourself with Visual Basic, its development environment and the toolset it offers, items such as serial communications, printer ports, bit-banging, protocol emulation, ISA, USB and Ethernet interfacing and the remote control of test-equipment over the GPIB bus, are covered in extent. Each topic is accompanied by clear, ready to run code, and where necessary, schematics are provided that will get your projects up to speed in no time. This book will show you advanced things like: using tools like Debug to find hardware addresses, setting up remote communication using TCP/IP and UDP sockets and even writing your own internet servers. Or how about connecting your own block of hardware over USB or Ethernet and controlling it from Visual Basic. Other things like internet-program communication, DDE and the new graphics interface of Windows XP are covered as well. All examples are ready to compile using Visual Basic 5.0, 6.0, NET or 2005. Extensive coverage is given on the differences between what could be called Visual Basic Classic and Visual basic .NET / 2005.
€ 39,95
Members € 31,96
-

Voltera Voltera Arduino Uno Templates (Pack of 6)
Build a custom Arduino Uno shield using the the Arduino Uno templates. Each pack contains six Arduino Uno templates. Downloads Gerber files
-
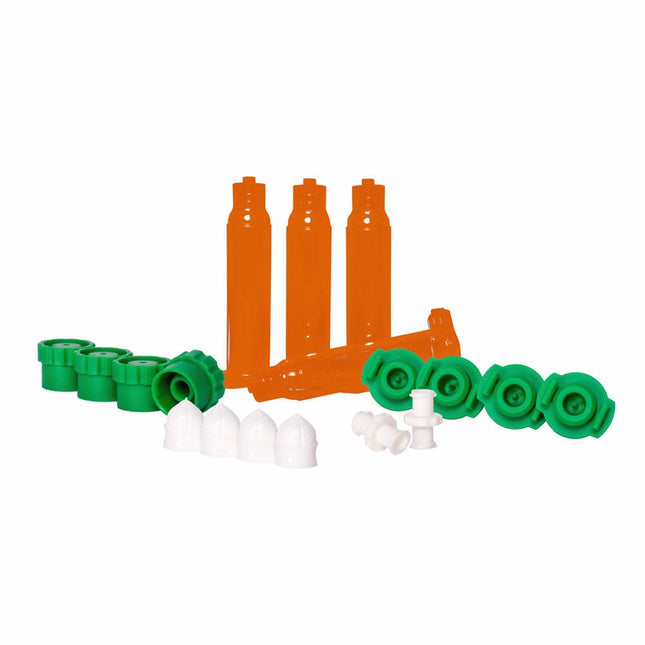

Voltera Voltera Cartridge Pack (UV Blocking)
Need to dispense your own UV sensitive fluids (up to 550nm)? Included 4x 5cc UV-Blocking Syringe Barrels 4x Standard Fit Pistons (white) 4x High Viscosity Fit Pistons (red) 4x Tip Caps 4x End Caps 2x Female to Female Luer couplers
-

Voltera Voltera Drill Bit Set
A set of high precision drill bits, covering the most common drill bit sizes. Just pop them in the V-One Drill with a 2.5 mm hex key (not included) and start drilling. The following sizes are included (2 of each): 0.70 mm 0.80 mm 0.90 mm 1.00 mm 1.60 mm
-
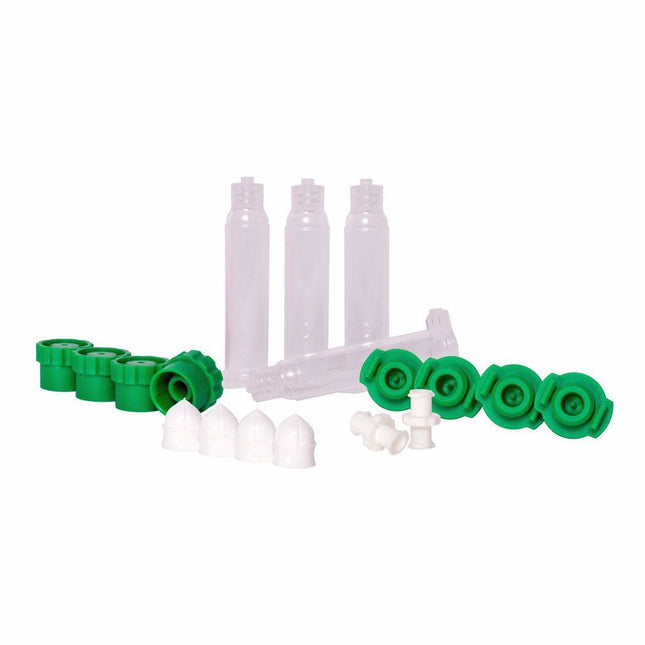

Voltera Voltera Empty Cartridge Pack (clear)
Get creative and dispense your own fluids with this pack of cartridges.
-
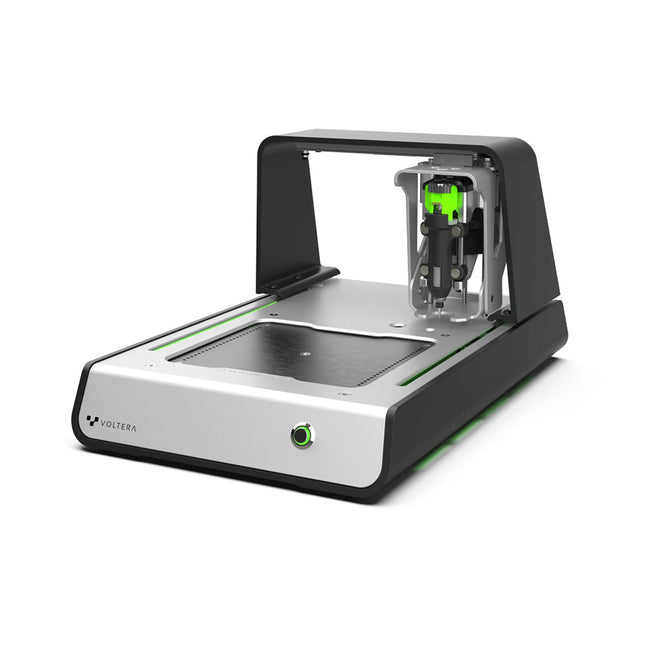

Voltera Voltera V-One Desktop PCB Printer
Solder Paste Dispensing and Reflow All-in-One The Voltera V-One creates two-layer prototype circuit boards on your desk. Gerber files go in, printed circuit boards come out. The dispenser lays down a silver-based conductive ink to print your circuit right before your eyes. Assembling traditional and additive boards is easy with the V-One’s solder paste dispensing and reflow features. Simply mount your board on the print bed and import your Gerber file into Voltera’s software. No more stencils required Voltera’s software is designed to be understood easily. From importing your Gerber files to the moment you press print, the software safely walks you through each step. Compatible with EAGLE, Altium, KiCad, Mentor Graphics, Cadence, DipTrace, Upverter. Included V-One PCB printer V-One dispenser V-One probe Nozzle pack Tip caps 3 x 4" FR1 substrate pack 2 x 3" FR1 substrate pack Substrate clamps Thumbscrew pack Hello World kit Solder wire Tweezers Power supply Power adapter Cables User guides Downloads Specifications V-One Software Manuals Safety Datasheets Technical Datasheets Voltera CAM file for EAGLE Substrates and Templates More Info Frequently Asked Questions More from the Voltera community Technical Specifications Printing Specifications Minimum trace width 0.2 mm Minimum passive size 1005 Minimum pin-to-pin pitch (conductive ink) 0.8 mml Minimum pin-to-pin pitch (solder paste) 0.5 mml Resistivity 12 mΩ/sq @ 70 um height Substrate material FR4 Maximum board thickness 3 mm Soldering Specifications Solder paste alloy Sn42/Bi57.6/Ag0.4 Solder wire alloy SnBiAg1 Soldering iron temperature 180-210°C Print Bed Print area 135 x 113.5 mm Max. heated bed temperature 240°C Heated bed ramp rate ~2°C/s Footprint Dimensions 390 x 257 x 207 mm (L x W x H) Weight 7 kg Computing Requirements Compatible operating systems Windows 7 or higher, MacOS 10.11 or higher Compatible file format Gerber Connection type Wired USB Certification EN 61326-1:2013 EMC requirements IEC 61010-1 Safety requirements CE Marking Affixed to the Voltera V-One printers delivered to European customers Designed and assembled in Canada. More technical information Quickstart Explore Flexible Printed Electronics on the V-One Voltera V-One Capabilities Reel Voltera V-One PCB Printer Walkthrough Unpacking the V-One V-One: Solder Paste Dispensing and Reflow All-in-One Voltera @ Stanford University's Bao Research Group: Robotic Skin and Stretchable Sensors Voltera @ Princeton: The Future of Aerospace Innovation
-

Waveshare Waveshare DVK600 FGPA CPLD Core Board
Waveshare DVK600 is an FPGA CPLD mother board that features expansion connectors for connecting FPGA CPLD core board and accessory boards. DVK600 provides an easy way to set up FPGA CPLD development system. Features FPGA CPLD core board connector: for easily connecting core boards which integrate an FPGA CPLD chip onboard 8I/Os_1 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 8I/Os_2 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 16I/Os_1 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 16I/Os_2 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 32I/Os_1 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 32I/Os_2 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules 32I/Os_3 interface, for connecting accessory boards/modules SDRAM interface for connecting SDRAM accessory board also works as FPGA CPLD pins expansion connectors LCD interface, for connecting LCD22, LCD12864, LCD1602 ONE-WIRE interface: easily connects to ONE-WIRE devices (TO-92 package), such as temperature sensor (DS18B20), electronic registration number (DS2401), etc. 5 V DC jack Joystick: five positions Buzzer Potentiometer: for LCD22 backlight adjustment, or LCD12864, LCD1602 contrast adjustment Power switch Buzzer jumper ONE-WIRE jumper Joystick jumper Downloads Schematics
€ 22,95€ 9,18
Members identical
-

Weller Weller WE1010 Digital Soldering Station (70 W)
High-quality soldering station with the most important tools and consumables, ideal for universal soldering applications. Features 1-Channel Power Unit, digital, 70 W Power unit, 1 channel with soldering iron WEP 70 and safety rest PH 70 70W solder iron with ergonomic handle and providing toolless tip change ESD safe station, iron and heat-resistant silicon cable for safe handling Using ET soldering tips Standby mode and auto setback conserves energy, protects equipment Password-protected to preserve settings Specifications Dimensions: 150 x 120 x 98 mm Weight: 1.4 kg Display: Digital LC Display Temperature range: Adjustable from 100°C - 450°C (200°F - 850°F) Voltage: 230 V Channels: 1 Temperature range (depends on tool) °C: 100-450 Temperature range (depends on tool) °F: 200-850 Temperature accuracy °C: Average tip temperature can be „offset“ to +/- 5°C at idle with no load Temperature accuracy °F: Average tip temperature can be „offset“ to +/- 9°F at idle with no load Temperature stability °C: ±6 Temperature stability °F: ±10 Heat-up time (ca) in seconds (50-350°C / 120-660°F): 28 sec. Heating output: 85 W
€ 157,60
-

Weller Weller WT1010 Digital Soldering Station (90 W)
High-quality soldering with the most important tools and consumables, ideal for universal soldering applications. Features Power unit, 1 channel 1-channel Soldering Station digital 90 W (95 W) WTP 90: The soldering iron for universal use with power response tips. Tip family XNT & THM (high mass tips) Lock function Specifications Dimensions W x D x H (mm): 149 x 138 x 101 Dimensions W x D x H (inch): 5.87 x 5.43 x 3.98 Weight (ca) in kg: 1.9 Channels: 1 Voltage: 230 V, 50/60 Hz Heating output: 90 W (95 W) Temperature accuracy °C: ±9 Display: Backlit LCD Temperature range: Adjustable from 50°C - 450°C (150°F - 850°C)Adjustable temperature range varies among tools Temperature stability °C: ±2 Temperature accuracy °F: ±17 Temperature stability °F: ±4 Temperature range (depends on tool) °C: 100-450 Temperature range (depends on tool) °F: 150-850 Equipotential balance: yes Fuse: 0,5 A WT compatible: yes ESD-safe: yes Power cord: EMEA
€ 538,45
-

Weller Weller WT1013 Digital Soldering Station (95 W)
The Weller WT 1013 soldering station set includes the WT 1 supply unit, the WP 80 soldering iron and the WSR 201 safety rest. It is stackable and thus creates more space in the workplace. With an integrated usage sensor, the soldering tool switches off automatically. Specifications Channels 1 Voltage 230 V Power 95 W Display Backlit LCD Temperature range 50 °C - 450 °C Temperature stability ±2 °C Temperature accuracy ±9 °C Fuse 0.5 A Equipotential bonding on WT compatible on ESD-safe on Power cable EMEA Dimensions 149 x 138 x 101 mm Weight (approx.) 1.9 kg
€ 441,65
-

Velleman Whadda 3D Xmas Tree Kit
The Whadda 3D Xmas Tree Kit is aimed at hobbyists and beginners who are interested in soldering and electronics. With this DIY kit, you can build a festive LED Christmas tree. Features 16 flashing red LEDs Extra green and yellow LEDs provided to customise your tree Can be hung on and fed through wires Will operate on 12 V DC (e.g. in cars) Specifications Low power consumption 8 mA Power supply 9 V battery operation (not included) Dimensions 102 x 88 x 80 mm Weight 65 g Downloads Manual
€ 10,95
-

Velleman Whadda Electronic Dice
This electronic dice with 7 red LEDs rolls when the push button is released and works with a 9 V battery (not included). Downloads Manual
€ 6,50
-
Elektor Publishing Wireless Power Design
From Theory to Practical Applications in Wireless Energy Transfer and Harvesting Wireless power transmission has gained significant global interest, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles and the Internet of Things (IoT). It’s a technology that allows the transfer of electricity without physical connections, offering solutions for everything from powering small devices over short distances to long-range energy transmission for more complex systems. Wireless Power Design provides a balanced mix of theoretical knowledge and practical insights, helping you explore the potential of wireless energy transfer and harvesting technologies. The book presents a series of hands-on projects that cover various aspects of wireless power systems, each accompanied by detailed explanations and parameter listings. The following five projects guide you through key areas of wireless power: Project 1: Wireless Powering of Advanced IoT Devices Project 2: Wireless Powered Devices on the Frontline – The Future and Challenges Project 3: Wireless Powering of Devices Using Inductive Technology Project 4: Wireless Power Transmission for IoT Devices Project 5: Charging Robot Crawler Inside the Pipeline These projects explore different aspects of wireless power, from inductive charging to wireless energy transmission, offering practical solutions for real-world applications. The book includes projects that use simulation tools like CST Microwave Studio and Keysight ADS for design and analysis, with a focus on practical design considerations and real-world implementation techniques.
€ 39,95
Members € 35,96
-

Elektor Digital Wireless Power Design (E-book)
From Theory to Practical Applications in Wireless Energy Transfer and Harvesting Wireless power transmission has gained significant global interest, particularly with the rise of electric vehicles and the Internet of Things (IoT). It’s a technology that allows the transfer of electricity without physical connections, offering solutions for everything from powering small devices over short distances to long-range energy transmission for more complex systems. Wireless Power Design provides a balanced mix of theoretical knowledge and practical insights, helping you explore the potential of wireless energy transfer and harvesting technologies. The book presents a series of hands-on projects that cover various aspects of wireless power systems, each accompanied by detailed explanations and parameter listings. The following five projects guide you through key areas of wireless power: Project 1: Wireless Powering of Advanced IoT Devices Project 2: Wireless Powered Devices on the Frontline – The Future and Challenges Project 3: Wireless Powering of Devices Using Inductive Technology Project 4: Wireless Power Transmission for IoT Devices Project 5: Charging Robot Crawler Inside the Pipeline These projects explore different aspects of wireless power, from inductive charging to wireless energy transmission, offering practical solutions for real-world applications. The book includes projects that use simulation tools like CST Microwave Studio and Keysight ADS for design and analysis, with a focus on practical design considerations and real-world implementation techniques.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Zhongdi ZD-11E PCB Holder
This adjustable circuit board holder is ideal for clamping PCB for soldering, desoldering or rework. Features 2 adjustable grips on a retractable stand to accommodate various board sizes. The adjustable clamps allow the PCB to rotate 360 degrees and stay set in any position. The base of this rigid metal stand features four rubber feet to ensure stability. Specifications Product size 30 x 16.5 x 12.5 cm Max. holding size 20 x 14 cm Weight 450 g
€ 7,95
-

Zhongdi ZD-129 Magnifying LED Desk Lamp
This desk lamp is ideal for your workplace. With the 5-inch 5D-lens, the finest work can be done. The lamp has 80 integrated LEDs. Features Lens size: 5 inch Lens material: glass Diopter: 5D Light source: T5 22 W fluorescent energy-saving bulb (80pcs LED) Standard mount: table base Voltage: 220-240 V Power: 22 W
€ 50,00
-

Zhongdi ZD-153A Solder Fume Extractor
Fumes released during the soldering process are potentially harmful to health. This solder fume extractor is securely fastened to the work table with a bracket. Thanks to the 3 axes, the solder fume extractor can be positioned perfectly, i.e. directly above the rising solder fumes. The harmful solder fumes are extracted by a powerful but quiet fan and filtered by an activated-carbon filter mat. Features Removes solder fumes Absorbs toxic gases and fumes from brazing operations Helps reduce the likelihood of headaches, eye irration and neusea Adjustable absorption angle for accurate placement Easy replaceable activated carbon filter High-performance fan Low noise and long life service Specifications Absorption capacity: 1 m³/min (max.) Power consumption: 23 W Power supply: 220-240 VAC Amount of activated carbon filter: 7 g Maximum absorption weight: 2 g Dimensions: 220 x 270 x 168 mm (W x H x D) Weight: 1.4 kg
€ 52,95
-

Zhongdi ZD-8962B ESD Soldering Station (70 W)
The ZD-8962B soldering station features an adjustable temperature range of 160°C to 480°C with an output power of 70 W. Equipped with an integrated heating element in the soldering tip, the station reaches the desired operating temperature in just 8 seconds. A large digital display provides real-time monitoring, showing both the preset target and the actual temperature of the iron for precision control. Additionally, the station is ESD-safe, ensuring sensitive electronic components are fully protected from electrostatic discharge during use. Specifications Power 70 W Input voltage 220-240 V AC/50 Hz Output voltage 20 V Temperature range 160°C – 480°C (320°F – 896°F) Heating time ~8 s Display Large, two-line LED display for showing target and actual temperature Special features ESD protection, Sleep mode/energy-saving function, Switch between °C and °F Included ZD-8962B Soldering station unit Soldering iron Soldering tip N12-1 Soldering iron stand with copper brush and sponge Soldering wire stand with lead-free soldering wire (10 g) Power cable (EU) Manual
€ 69,95€ 59,95
Members identical
-

Zhongdi ZD-8965 Desoldering Station
The ZD-8965 is a digital temperature-controlled desoldering station equipped with ground protection and an LCD screen for temperature display. Despite its compact and robust design, this high-power desoldering station is easy to operate with just one hand. The ZD-8965 features a soldering gun with an integrated filter that captures any extracted material, allowing for continuous operation by simply replacing the filters. Additionally, a temperature sensor is embedded in the tip, enabling rapid response to temperature fluctuations for consistent performance. Features Effortlessly adjust the temperature between 160°C and 480°C using the convenient up/down buttons on the front panel. LED display to indicate the temperature in °C/°F Features an ergonomic pistol grip with a trigger for quick and efficient solder waste removal. The upgraded soldering gun includes a rear trigger, making it exceptionally convenient for replacing and cleaning components. Comes with a high-quality soldering gun and a sturdy holder. Equipped with a heavy-duty heater that ensures optimal desoldering performance every time. Specifications Station Voltage supply 220-240 V Power 140 W Vakuum pressure 600 mm HG Desoldering Gun Power 140 W (18 V DC)Heat up rating: 140 W Temperature 160-480°C (320-896°F) Heating element Ceramic heater Included 1x ZD-8965 Desoldering station 2x Spare soldering tips 3x Cleaning needles for desoldering tips 3x Spare filter for desoldering gun 1x Spare filter for desoldering station 1x Manual
€ 99,00
-

Zhongdi ZD-915 Desoldering Station
The ZD-915 is a digital desoldering station with ESD protection and digital display of both the actual and set value on an LCD screen. This desoldering station has high power in a compact and robust housing and makes desoldering easy, because it can be operated with one hand. The ZD-915 features a soldering gun that houses a filter that catches any sucked material, so you only need to replace the filters to continue. There is also a temperature sensor in the tip so that temperature fluctuations can be quickly absorbed. Features The temperature is easily adjusted by simple up/down buttons. 140 W temperature controlled soldering station with adjustable range from 160°C to 480°C. The desoldering station is designed for lead free desoldering specially. The side of the station features a typical holder with sponge. An illuminated power on/off is also loacted on the front. Specifications Station Voltage supply 220-240 V Power consumption 140 W Vakuum pressure 600 mm HG Desoldering Gun Power consumption 24 V AC 80 WHeat up rating 130 W Temperature 160-480 °C Heating element Ceramic heater Included 1x ZD-915 Desoldering station 2x Spare soldering tip 3x Cleaning needle for desoldering tips 1x Spare filter for desoldering gun 1x Manual
€ 107,00























