Products
-

Elektor Publishing Control Your Home with Raspberry Pi
Secure, Modular, Open-Source and Self-Sufficient Ever since the Raspberry Pi was introduced, it has been used by enthusiasts to automate their homes. The Raspberry Pi is a powerful computer in a small package, with lots of interfacing options to control various devices. This book shows you how you can automate your home with a Raspberry Pi. You’ll learn how to use various wireless protocols for home automation, such as Bluetooth, 433.92 MHz radio waves, Z-Wave, and Zigbee. Soon you’ll automate your home with Python, Node-RED, and Home Assistant, and you’ll even be able to speak to your home automation system. All this is done securely, with a modular system, completely open-source, without relying on third-party services. You’re in control of your home, and no one else. At the end of this book, you can install and configure your Raspberry Pi as a highly flexible home automation gateway for protocols of your choice, and link various services with MQTT to make it your own system. This DIY (do it yourself) approach is a bit more laborious than just installing an off-the-shelf home automation system, but in the process, you can learn a lot, and in the end, you know exactly what’s running your house and how to tweak it. This is why you were interested in the Raspberry Pi in the first place, right? Turn your Raspberry Pi into a reliable gateway for various home automation protocols. Make your home automation setup reproducible with Docker Compose. Secure all your network communication with TLS. Create a video surveillance system for your home. Automate your home with Python, Node-RED, Home Assistant and AppDaemon. Securely access your home automation dashboard from remote locations. Use fully offline voice commands in your own language. Downloads Errata on GitHub
€ 44,95
Members € 40,46
-

Elektor Digital Control Your Home with Raspberry Pi (E-book)
Secure, Modular, Open-Source and Self-Sufficient Ever since the Raspberry Pi was introduced, it has been used by enthusiasts to automate their homes. The Raspberry Pi is a powerful computer in a small package, with lots of interfacing options to control various devices. This book shows you how you can automate your home with a Raspberry Pi. You’ll learn how to use various wireless protocols for home automation, such as Bluetooth, 433.92 MHz radio waves, Z-Wave, and Zigbee. Soon you’ll automate your home with Python, Node-RED, and Home Assistant, and you’ll even be able to speak to your home automation system. All this is done securely, with a modular system, completely open-source, without relying on third-party services. You’re in control of your home, and no one else. At the end of this book, you can install and configure your Raspberry Pi as a highly flexible home automation gateway for protocols of your choice, and link various services with MQTT to make it your own system. This DIY (do it yourself) approach is a bit more laborious than just installing an off-the-shelf home automation system, but in the process, you can learn a lot, and in the end, you know exactly what’s running your house and how to tweak it. This is why you were interested in the Raspberry Pi in the first place, right? Turn your Raspberry Pi into a reliable gateway for various home automation protocols. Make your home automation setup reproducible with Docker Compose. Secure all your network communication with TLS. Create a video surveillance system for your home. Automate your home with Python, Node-RED, Home Assistant and AppDaemon. Securely access your home automation dashboard from remote locations. Use fully offline voice commands in your own language. Download the software and view the errata for the book on GitHub.
€ 34,95
Members € 27,96
-

Elektor Digital Controller Area Network Projects (E-book)
The Controller Area Network (CAN) was originally developed to be used as a vehicle data bus system in passenger cars. Today, CAN controllers are available from over 20 manufacturers, and CAN is finding applications in other fields, such as medical, aerospace, process control, automation, and so on. This book is written for students, for practising engineers, for hobbyists, and for everyone else who may be interested to learn more about the CAN bus and its applications. The aim of this book is to teach you the basic principles of CAN networks and in addition the development of microcontroller based projects using the CAN bus. In summary, this book enables the reader to: Learn the theory of the CAN bus used in automotive industry Learn the principles, operation, and programming of microcontrollers Design complete microcontroller based projects using the C language Develop complete real CAN bus projects using microcontrollers Learn the principles of OBD systems used to debug vehicle electronics You will learn how to design microcontroller based CAN bus nodes, build a CAN bus, develop high-level programs, and then exchange data in real-time over the bus. You will also learn how to build microcontroller hardware and interface it to LEDs, LCDs, and A/D converters. The book assumes that the reader has some knowledge on basic electronics. Knowledge of the C programming language will be useful in later chapters of the book, and familiarity with at least one member of the PIC series of microcontrollers will be an advantage, especially if the reader intends to develop microcontroller based projects using the CAN bus.
€ 29,95
Members € 23,96
-

Elektor Digital Controller Area Network Projects with ARM and Arduino (E-book)
This book details the use of the ARM Cortex-M family of processors and the Arduino Uno in practical CAN bus based projects. Inside, it gives a detailed introduction to the architecture of the Cortex-M family whilst providing examples of popular hardware and software development kits. Using these kits helps to simplify the embedded design cycle considerably and makes it easier to develop, debug, and test a CAN bus based project. The architecture of the highly popular ARM Cortex-M processor STM32F407VGT6 is described at a high level by considering its various modules. In addition, the use of the mikroC Pro for ARM and Arduino Uno CAN bus library of functions are described in detail. This book is written for students, for practising engineers, for hobbyists, and for everyone else who may need to learn more about the CAN bus and its applications. The book assumes that the reader has some knowledge of basic electronics. Knowledge of the C programming language will be useful in later chapters of the book, and familiarity with at least one microcontroller will be an advantage, especially if the reader intends to develop microcontroller based projects using CAN bus. The book should be useful source of reference to anyone interested in finding an answer to one or more of the following questions: What bus systems are available for the automotive industry? What are the principles of the CAN bus? What types of frames (or data packets) are available in a CAN bus system? How can errors be detected in a CAN bus system and how reliable is a CAN bus system? What types of CAN bus controllers are there? What are the advantages of the ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers? How can one create a CAN bus project using an ARM microcontroller? How can one create a CAN bus project using an Arduino microcontroller? How can one monitor data on the CAN bus?
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Cytron Cytron Maker Line Sensor
Maker Line is a line sensor with 5 x IR sensors array that is able to track line from 13 mm to 30 mm width. The sensor calibration is also simplified. There is no need to adjust the potentiometer for each IR sensor. You just have to press the calibrate button for 2 seconds to enter calibration mode. Afterwards you need to sweep the sensors array across the line, press the button again and you are good to go. The calibration data is saved in EEPROM and it will stay intact even if the sensor has been powered off. Thus, calibration only needs to be carried out once unless the sensor height, line color or background color has changed. Maker Line also supports dual outputs: 5 x digital outputs for the state of each sensor independently, which is similar to conventional IR sensor, but you get the benefit of easy calibration, and also one analog output, where its voltage represents the line position. Analog output also offers higher resolution compared to individual digital outputs. This is especially useful when high accuracy is required while building a line following robot with PID control. Features Operating Voltage: DC 3.3 V and 5 V compatible (with reverse polarity protection) Recommended Line Width: 13 mm to 30 mm Selectable line color (light or dark) Sensing Distance (Height): 4 mm to 40 mm (Vcc = 5 V, Black line on white surface) Sensor Refresh Rate: 200 Hz Easy calibration process Dual Output Types: 5 x digital outputs represent each IR sensor state, 1 x analog output represents line position. Support wide range of controllers such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi etc. Downloads Datasheet Tutorial: Building A Low-Cost Line Following Robot
€ 14,95€ 5,98
Members identical
-
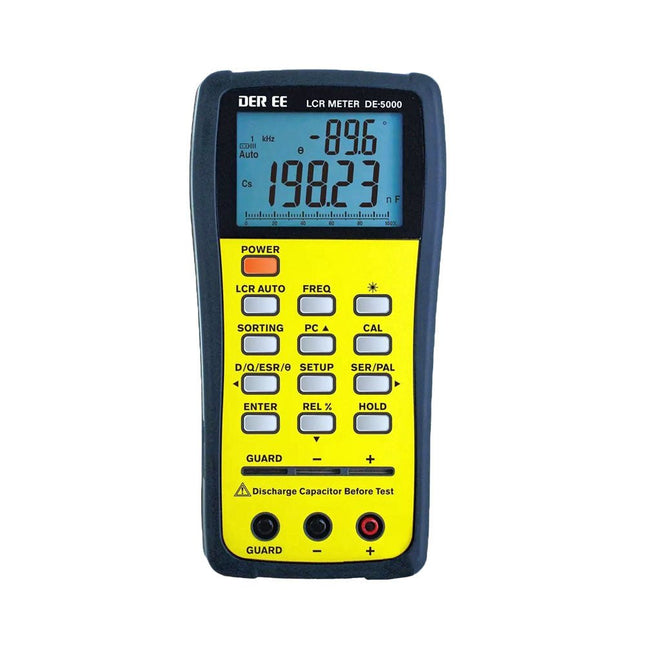

DER EE DER EE DE-5000 LCR Meter (100 kHz)
The DE-5000 is a smart, high-accurate, flexible and easy-to-use portable LCR meter. It features automatic LCR check, 4-wire Kelvin measurement, backlit display with 19999/1999 counts, multiple measurement modes and selectable test frequencies (100 Hz, 120 Hz, 1 kHz, 10 kHz or 100 kHz). The DE-5000 LCR meter is a practical helper for engineers or technicians. Features Auto L.C.R. check Ls/Lp/Cs/Cp/Rs/Rp/DCR with D/Q/θ/ESR measurement 4-wire Kelvin measurement 20,000 / 2,000 counts display Backlight Relative mode Series / Parallel modes Components sorting function Low battery indication Auto power off Specifications Test frequency 100 Hz / 120 Hz / 1 kHz / 10 kHz / 100 kHz Resistance range 20.000 Ω – 200.0 MΩ DCR range 200.00 Ω – 200.0 MΩ Capacitance range 200.00 pF – 20.00 mF Inductance range 20.000 µH – 2.000 KH Display (backlit LCD) 19999 / 1999 counts Selectable tolerance ±0.25%, ±0.5%, ±1%, ±2%, ±5%, ±10%, ±20% Power supply 9 V battery Dimensions 188 x 95 x 52 mm Weight 350 g (excluding battery) Included DE-5000 LCR meter Alligator test lead case (TL-21) AC/DC adaptor Guard line (TL-23) TL-22 SMD tweezers 9 V battery Carrying case Manual Downloads Datasheet
€ 192,39
-
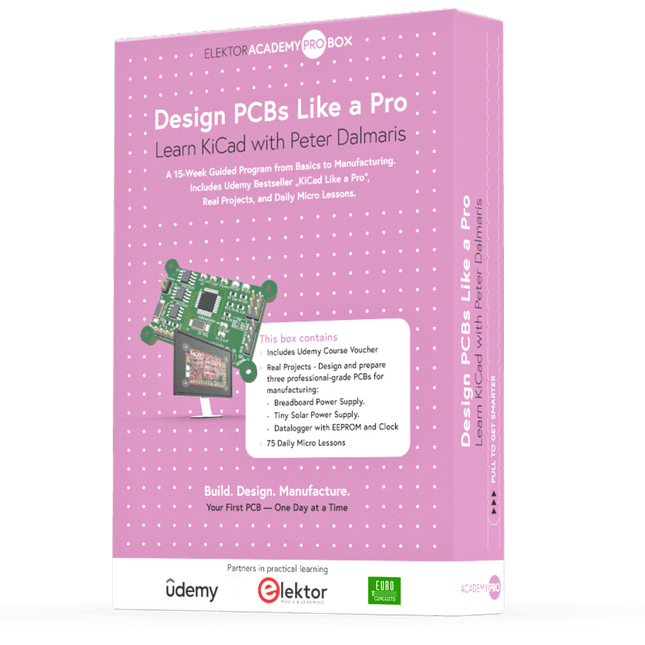
Elektor Academy Pro Design PCBs Like a Pro
Learn KiCad with Peter Dalmaris The Academy Pro Box "Design PCBs like a Pro" offers a complete, structured training programme in PCB design, combining online learning with practical application. Based on Peter Dalmaris’ KiCad course, the 15-week programme integrates video lessons, printed materials (2 books), and hands-on projects to ensure participants not only understand the theory but also develop the skills to apply it in practice. Unlike standard courses, the Academy Pro Box provides a guided learning path with weekly milestones and physical components to design, test, and produce working PCBs. This approach supports a deeper learning experience and better knowledge retention. The box is ideal for engineers, students, and professionals who want to develop practical PCB design expertise using open-source tools. With the added option to have their final project manufactured, participants complete the programme with real results – ready for use, testing, or further development. Learn by doing Build skills. Design real boards. Generate Gerbers. Place your first order. This isn’t just a course – it’s a complete project journey from idea to product. You’ll walk away with: Working knowledge of KiCad’s tools Confidence designing your own PCBs A fully manufacturable circuit board – made by you What's inside the Box (Course)? Both volumes of "KiCad Like a Pro" (valued at €105) Vol 1: Fundamentals and Projects Vol 2: Advanced Projects and Recipes Coupon code to join the bestselling KiCad 9 online course by Peter Dalmaris on Udemy, featuring 20+ hours of video training. You'll complete three full design projects: Breadboard Power Supply Tiny Solar Power Supply Datalogger with EEPROM and Clock Voucher from Eurocircuits for the production of PCBs (worth €85 excl. VAT) Learning Material (of this Box/Course) 15-Week Learning Program ▶ Click here to open Week 1: Setup, Fundamentals, and First Steps in PCB Design Week 2: Starting Your First PCB Project – Schematic Capture Week 3: PCB Layout – From Netlist to Board Design Week 4: Design Principles, Libraries, and Workflow Week 5: Your First Real-World PCB Project Week 6: Custom Libraries – Symbols, Footprints, and Workflow Week 7: Advanced Tools – Net Classes, Rules, Zones, Routing Week 8: Manufacturing Files, BOMs, and PCB Ordering Week 9: Advanced Finishing Techniques – Graphics, Refinement, and Production Quality Week 10: Tiny Solar Power Supply – From Schematic to Layout Week 11: Tiny Solar Power Supply – PCB Layout and Production Prep Week 12: ESP32 Clone Project – Schematic Design and Layout Prep Week 13: ESP32 Clone – PCB Layout and Manufacturing Prep Week 14: Final Improvements and Advanced Features Week 15: Productivity Tools, Simulation, and Automation KiCad Course with 18 Lessons on Udemy (by Peter Dalmaris) ▶ Click here to open Introduction Getting started with PCB design Getting started with KiCad Project: A hands-on tour of KiCad (Schematic Design) Project: A hands-on tour of KiCad (Layout) Design principles and PCB terms Design workflow and considerations Fundamental KiCad how-to: Symbols and Eeschema Fundamental KiCad how-to: Footprints and Pcbnew Project: Design a simple breadboard power supply PCB Project: Tiny Solar Power Supply Project: MCU datalogger with build-in 512K EEPROM and clock Recipes KiCad 9 new features and improvements Legacy (from previous versions of KiCad) KiCad 7 update (Legacy) (Legacy) Gettings started with KiCad Bonus lecture About the Author Dr. Peter Dalmaris, PhD is an educator, an electrical engineer and Maker. Creator of online video courses on DIY electronics and author of several technical books. As a Chief Tech Explorer since 2013 at Tech Explorations, the company he founded in Sydney, Australia, Peter's mission is to explore technology and help educate the world. What is Elektor Academy Pro? Elektor Academy Pro delivers specialized learning solutions designed for professionals, engineering teams, and technical experts in the electronics and embedded systems industry. It enables individuals and organizations to expand their practical knowledge, enhance their skills, and stay ahead of the curve through high-quality resources and hands-on training tools. From real-world projects and expert-led courses to in-depth technical insights, Elektor empowers engineers to tackle today’s electronics and embedded systems challenges. Our educational offerings include Academy Books, Pro Boxes, Webinars, Conferences, and industry-focused B2B magazines – all created with professional development in mind. Whether you're an engineer, R&D specialist, or technical decision-maker, Elektor Academy Pro bridges the gap between theory and practice, helping you master emerging technologies and drive innovation within your organization.
€ 199,95€ 164,95
Members identical
-

Elektor Digital Design your own Embedded Linux Control Centre (E-book)
This book is all about building your own DIY home control system. It presents two innovative ways to assemble such a system: By recycling old PC hardware – possibly extending the life of an old PC, or by using Raspberry Pi. In both cases, the main system outlined in this book will consist of a computer platform, a wireless mains outlet, a controller and a USB webcam – All linked together by Linux. By using the Raspberry Pi in conjunction with Arduino (used as an advanced I/O system board), it is possible to construct a small, compact, embedded control system offering enhanced capacity for USB integration, webcams, thermal monitoring and communication with the outside world. The experience required to undertake the projects within this book are minimal exposure to PC hardware and software, the ability to surf the internet, burn a CD-ROM and assemble a small PCB.
€ 34,95
Members € 27,96
-

Elektor Digital Designing Tube Amplifiers (E-book)
This book focuses more on practical aspects than on theory, and it has an contemplative nature, as though the author were viewing amplifiers from above. Knowledge elements are integrated and placed in the context of a broad overview. Even now tube amplifiers still sound great perhaps better than ever before. In part that is because we now have access to modern components such as toroidal output transformers, extremely high-quality resistors and capacitors, and many sorts of wire with good acoustic properties. Modern audio sources, such as CD players, and the latest top-end loudspeakers also enable us to appreciate how well tube amplifiers reproduce music even better than before. This new book from Menno van der Veen looks at tube amplifiers from more than just a theoretical perspective. It focuses primarily on the design phase, where decisions must be taken with regard to the purpose and requirements of the amplifier, and it addresses the following questions: How do these aspects relate to subjective and objective criteria? Which circuits sound the best, and why? If you want to develop and market an amplifier, what problems should you expect? What are the significance and meaning of measurements? Are they still meaningful, or have they lost their relevance? Thanks to the enormous processing power of computers, we can now measure more details than ever before. How can these new methods be applied to tube amplifiers? Previously it was sufficient to measure the frequency range, power and distortion of an amplifier in order to characterize the amplifier. Are these measurements still sufficient, or should we start measuring according to how we hear, using real music signals instead of waveforms from signal generators? The author sketches a future where amplifier measurements that conform to our sense of hearing enable us to arrive at new insights. This book focuses more on practical aspects than on theory, and it has an contemplative nature, as though the author were viewing amplifiers from above. Knowledge elements are integrated and placed in the context of a broad overview.
€ 29,95
Members € 23,96
-

Elektor Digital Develop and Operate Your LoRaWAN IoT Nodes (E-book)
Ready-to-use devices and self-built Arduino nodes in the 'The Things Network' LoRaWAN has developed excellently as a communication solution in the IoT. The Things Network (TTN) has contributed to this. The Things Network was upgraded to The Things Stack Community Edition (TTS (CE)). The TTN V2 clusters were closed towards the end of 2021. This book shows you the necessary steps to operate LoRaWAN nodes using TTS (CE) and maybe extend the network of gateways with an own gateway. Meanwhile, there are even LoRaWAN gateways suitable for mobile use with which you can connect to the TTN server via your cell phone. The author presents several commercial LoRaWAN nodes and new, low-cost and battery-powered hardware for building autonomous LoRaWAN nodes. Registering LoRaWAN nodes and gateways in the TTS (CE), providing the collected data via MQTT and visualization via Node-RED, Cayenne, Thingspeak, and Datacake enable complex IoT projects and completely new applications at very low cost. This book will enable you to provide and visualize data collected with battery-powered sensors (LoRaWAN nodes) wirelessly on the Internet. You will learn the basics for smart city and IoT applications that enable, for example, the measurement of air quality, water levels, snow depths, the determination of free parking spaces (smart parking), and the intelligent control of street lighting (smart lighting), among others.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Elektor Publishing Develop your own Bluetooth Low Energy Applications
For Raspberry Pi, ESP32 and nRF52 with Python, Arduino and Zephyr Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) radio chips are ubiquitous from Raspberry Pi to light bulbs. BLE is an elaborate technology with a comprehensive specification, but the basics are quite accessible. A progressive and systematic approach will lead you far in mastering this wireless communication technique, which is essential for working in low power scenarios. In this book, you’ll learn how to: Discover BLE devices in the neighborhood by listening to their advertisements. Create your own BLE devices advertising data. Connect to BLE devices such as heart rate monitors and proximity reporters. Create secure connections to BLE devices with encryption and authentication. Understand BLE service and profile specifications and implement them. Reverse engineer a BLE device with a proprietary implementation and control it with your own software. Make your BLE devices use as little power as possible. This book shows you the ropes of BLE programming with Python and the Bleak library on a Raspberry Pi or PC, with C++ and NimBLE-Arduino on Espressif’s ESP32 development boards, and with C on one of the development boards supported by the Zephyr real-time operating system, such as Nordic Semiconductor's nRF52 boards. Starting with a very little amount of theory, you’ll develop code right from the beginning. After you’ve completed this book, you’ll know enough to create your own BLE applications.
€ 39,95
Members € 35,96
-

Elektor Digital Develop your own Bluetooth Low Energy Applications (E-book)
For Raspberry Pi, ESP32 and nRF52 with Python, Arduino and Zephyr Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) radio chips are ubiquitous from Raspberry Pi to light bulbs. BLE is an elaborate technology with a comprehensive specification, but the basics are quite accessible. A progressive and systematic approach will lead you far in mastering this wireless communication technique, which is essential for working in low power scenarios. In this book, you’ll learn how to: Discover BLE devices in the neighborhood by listening to their advertisements. Create your own BLE devices advertising data. Connect to BLE devices such as heart rate monitors and proximity reporters. Create secure connections to BLE devices with encryption and authentication. Understand BLE service and profile specifications and implement them. Reverse engineer a BLE device with a proprietary implementation and control it with your own software. Make your BLE devices use as little power as possible. This book shows you the ropes of BLE programming with Python and the Bleak library on a Raspberry Pi or PC, with C++ and NimBLE-Arduino on Espressif’s ESP32 development boards, and with C on one of the development boards supported by the Zephyr real-time operating system, such as Nordic Semiconductor's nRF52 boards. Starting with a very little amount of theory, you’ll develop code right from the beginning. After you’ve completed this book, you’ll know enough to create your own BLE applications.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-
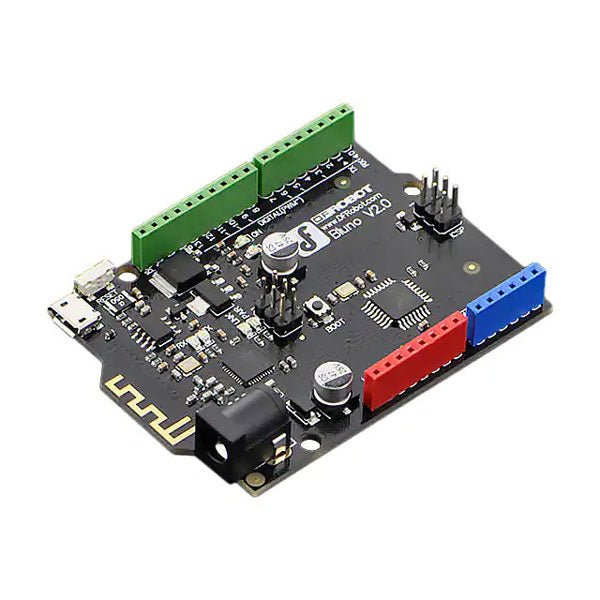

DFRobot DFRobot Bluno – Arduino-compatible Board with Bluetooth 4.0
Bluno is the first of its kind in integrating Bluetooth 4.0 (BLE) module into Arduino Uno, making it an ideal prototyping platform for both software and hardware developers to go BLE. You will be able to develop your own smart bracelet, smart pedometer, and more. Through the low-power Bluetooth 4.0 technology, real-time low energy communication can be made really easy. Bluno integrates a TI CC2540 BT 4.0 chip with the Arduino UNno. It allows wireless programming via BLE, supports Bluetooth HID, AT command to config BLE and you can upgrade BLE firmware easily. Bluno is also compatible with all 'Arduino Uno' pins which means any project made with Uno can directly go wireless! Specifications On-board BLE chip: TI CC2540 Wireless Programming via BLE Support Bluetooth HID Support AT command to config the BLE Transparent communication through Serial Upgrade BLE firmware easily DC Supply: USB Powered or External 7~12 V DC Microcontroller: Atmega328 Bootloader: Arduino Uno ( disconnect any BLE device before uploading a new sketch ) Compatible with the Arduino Uno pin mapping Size: 60 x 53 mm(2.36 x 2.08') Weight: 30 g
€ 34,95€ 13,98
Members identical
-
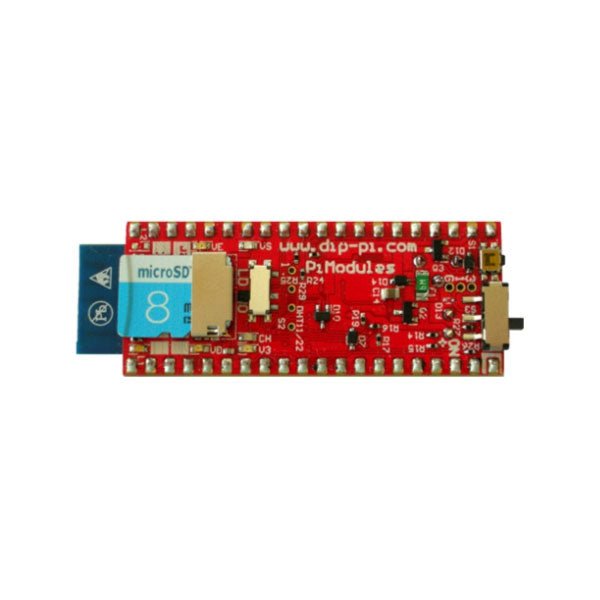

Pi Modules DiP-Pi Pico PIoT for Raspberry Pi Pico
The DiP-Pi PIoT is an Advanced Powered, WiFi connectivity System with sensors embedded interfaces that cover most of possible needs for IoT application based on Raspberry Pi Pico. It can supply the system with up to 1.5 A @ 4.8 V delivered from 6-18 VDC on various powering schemes like Cars, Industrial plant etc., additionally to original micro-USB of the Raspberry Pi Pico. It supports LiPo or Li-Ion Battery with Automatic Charger as also automatic switching from cable powering to battery powering or reverse (UPS functionality) when cable powering lost. Extended Powering Source (EPR) is protected with PPTC Resettable fuse, Reverse Polarity, as also ESD. The DiP-Pi PIoT contains Raspberry Pi Pico embedded RESET button as also ON/OFF Slide Switch that is acting on all powering sources (USB, EPR or Battery). User can monitor (via Raspberry Pi Pico A/D pins) battery level and EPR Level with PICO’s A/D converters. Both A/D inputs are bridged with 0402 resistors (0 OHM) therefore if for any reason user needs to use those Pico pins for their own application can be easy removed. The charger is automatically charging connected battery (if used) but in addition user can switch charger ON/OFF if their application needs it. DiP-Pi PIoT can be used for cable powered IoT systems, but also for pure Battery Powered System with ON/OFF. Each powering source status is indicated by separate informative LEDs (VBUS, VSYS, VEPR, CHGR, V3V3). User can use any capacity of LiPo or Li-Ion type; however, must take care to use PCB protected batteries with max discharge current allowed of 2 A. The embedded battery charger is set to charge battery with 240 mA current. This current is set by resistor so if user need more/less can himself to change it. The DiP-Pi PIoT is also equipped with WiFi ESP8266 Clone module with embedded antenna. This feature open a wide range of IoT applications based on it. In Addition to all above features DiP-Pi PIoT is equipped with embedded 1-wire, DHT11/22 sensors, and micro–SD Card interfaces. Combination of the extended powering, battery, and sensors interfaces make the DiP-Pi PIoT ideal for IoT applications like data logger, plants monitoring, refrigerators monitoring etc. DiP-Pi PIoT is supported with plenty of ready to use examples written in Micro Python or C/C++. Specifications General Dimensions 21 x 51 mm Raspberry Pi Pico pinout compatible Independent Informative LEDs (VBUS, VSYS, VEPR, CHGR, V3V3) Raspberry Pi Pico RESET Button ON/OFF Slide Switch acting on all powering sources (USB, EPR, Battery) External Powering 6-18 VDC (Cars, Industrial Applications etc.) External Power (6-18 VDC) Level Monitoring Battery Level Monitoring Inverse Polarity Protection PPTC Fuse Protection ESD Protection Automatic Battery Charger (for PCB protected LiPo, Li-Ion – 2 A Max) Automatic/User Control Automatic Switch from Cable Powering to Battery Powering and reverse (UPS Functionality) Various powering schemes can be used at the same time with USB Powering, External Powering and Battery Powering 1.5 A @ 4.8 V Buck Converter on EPR Embedded 3.3 V @ 600 mA LDO ESP8266 Clone WiFi Connectivity ESP8266 Firmware Upload Switch Embedded 1-wire Interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Powering Options Raspberry Pi Pico micro-USB (via VBUS) External Powering 6-18 V (via dedicated Socket – 3.4/1.3 mm) External Battery Supported Battery Types LiPo with protection PCB max current 2A Li-Ion with protection PCB max current 2A Embedded Peripherals and Interfaces Embedded 1-wire interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Micro SD Card Socket Programmer Interface Standard Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ Standard Raspberry Pi Pico Micro Python Case Compatibility DiP-Pi Plexi-Cut Case System Monitoring Battery Level via Raspberry Pi Pico ADC0 (GP26) EPR Level via Raspberry Pi Pico ADC1 (GP27) Informative LEDs VB (VUSB) VS (VSYS) VE (VEPR) CH (VCHR) V3 (V3V3) System Protection Direct Raspberry Pi Pico Hardware Reset Button ESD Protection on EPR Reverse Polarity Protection on EPR PPTC 500 mA @ 18 V fuse on EPR EPR/LDO Over Temperature protection EPR/LDO Over Current protection System Design Designed and Simulated with PDA Analyzer with one of the most advanced CAD/CAM Tools – Altium Designer Industrial Originated PCB Construction 2 ozcopper PCB manufactured for proper high current supply and cooling 6 mils track/6 mils gap technology 2 layers PCB PCB Surface Finishing – Immersion Gold Multi-layer Copper Thermal Pipes for increased System Thermal Response and better passive cooling Downloads Datasheet Manual
€ 21,95€ 8,78
Members identical
-
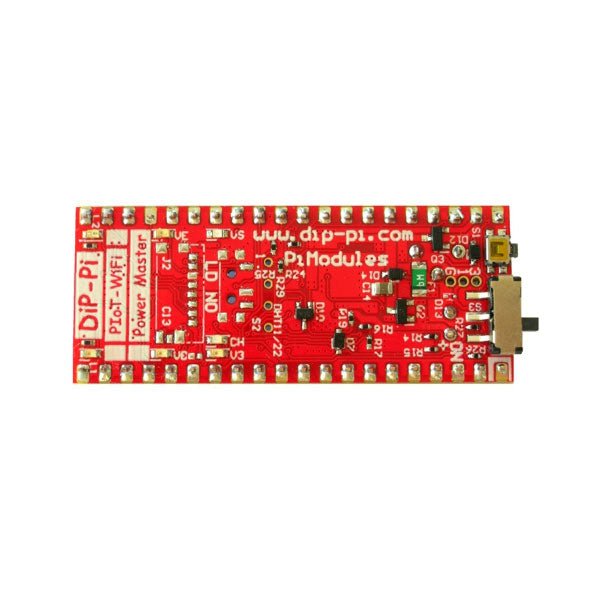

Pi Modules DiP-Pi Pico Power Master for Raspberry Pi Pico
The DiP-Pi Power Master is an Advanced Powering System with embedded sensors interfaces that cover most of possible needs for application based on Raspberry Pi Pico. It can supply the system with up to 1.5 A @ 4.8 V delivered from 6-18 VDC on various powering schemes like Cars, Industrial plant etc., additionally to original micro-USB of the Raspberry Pi Pico. It supports LiPo or Li-Ion Battery with Automatic Charger as also automatic switching from cable powering to battery powering or reverse (UPS functionality) when cable powering lost. Extended Powering Source (EPR) is protected with PPTC Resettable fuse, Reverse Polarity, as also ESD. The DiP-Pi Power Master contains Raspberry Pi Pico embedded RESET button as also ON/OFF Slide Switch that is acting on all powering sources (USB, EPR or Battery). User can monitor (via Raspberry Pi Pico A/D pins) battery level and EPR Level with PICO’s A/D converters. Both A/D inputs are bridged with 0402 resistors (0 OHM) therefore if for any reason user needs to use those Pico pins for their own application can be easy removed. The charger is automatically charging connected battery (if used) but in addition user can switch charger ON/OFF if their application needs it. DiP-Pi Power Master can be used for cable powered systems, but also for pure Battery Powered System with ON/OFF. Each powering source status is indicated by separate informative LEDs (VBUS, VSYS, VEPR, CHGR, V3V3). User can use any capacity of LiPo or Li-Ion type; however, must take care to use PCB protected batteries with max discharge current allowed of 2 A. The embedded battery charger is set to charge battery with 240 mA current. This current is set by resistor so if user need more/less can himself to change it. In Addition to all above features DiP-Pi Power Master is equipped with embedded 1-wire and DHT11/22 sensors interfaces. Combination of the extended powering, battery, and sensors interfaces make the DiP-Pi Power Master ideal for applications like data logger, plants monitoring, refrigerators monitoring etc. DiP-Pi Power Master is supported with plenty of ready to use examples written in Micro Python or C/C++. Specifications General Dimensions 21 x 51 mm Raspberry Pi Pico pinout compatible Independent Informative LEDs (VBUS, VSYS, VEPR, CHGR, V3V3) Raspberry Pi Pico RESET Button ON/OFF Slide Switch acting on all powering sources (USB, EPR, Battery) External Powering 6-18 V DC (Cars, Industrial Applications etc.) External Power (6-18 VDC) Level Monitoring Battery Level Monitoring Inverse Polarity Protection PPTC Fuse Protection ESD Protection Automatic Battery Charger (for PCB protected LiPo, Li-Ion – 2 A Max) Automatic/User Control Automatic Switch from Cable Powering to Battery Powering and reverse (UPS Functionality) Various powering schemes can be used at the same time with USB Powering, External Powering and Battery Powering 1.5 A @ 4.8 V Buck Converter on EPR Embedded 3.3 V @ 600mA LDO Embedded 1-wire Interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Powering Options Raspberry Pi Pico micro-USB (via VBUS) External Powering 6-18 V (via dedicated Socket – 3.4/1.3 mm) External Battery Supported Battery Types LiPo with protection PCB max current 2A Li-Ion with protection PCB max current 2A Embedded Peripherals and Interfaces Embedded 1-wire interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Programmer Interface Standard Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ Standard Raspberry Pi Pico Micro Python Case Compatibility DiP-Pi Plexi-Cut Case System Monitoring Battery Level via Raspberry Pi Pico ADC0 (GP26) EPR Level via Raspberry Pi Pico ADC1 (GP27) Informative LEDs VB (VUSB) VS (VSYS) VE (VEPR) CH (VCHR) V3 (V3V3) System Protection Direct Raspberry Pi Pico Hardware Reset Button ESD Protection on EPR Reverse Polarity Protection on EPR PPTC 500 mA @ 18 V fuse on EPR EPR/LDO Over Temperature protection EPR/LDO Over Current protection System Design Designed and Simulated with PDA Analyzer with one of the most advanced CAD/CAM Tools – Altium Designer Industrial Originated PCB Construction 2 ozcopper PCB manufactured for proper high current supply and cooling 6 mils track/6 mils gap technology 2 layers PCB PCB Surface Finishing – Immersion Gold Multi-layer Copper Thermal Pipes for increased System Thermal Response and better passive cooling Downloads Datasheet Datasheet
€ 17,95€ 7,18
Members identical
-
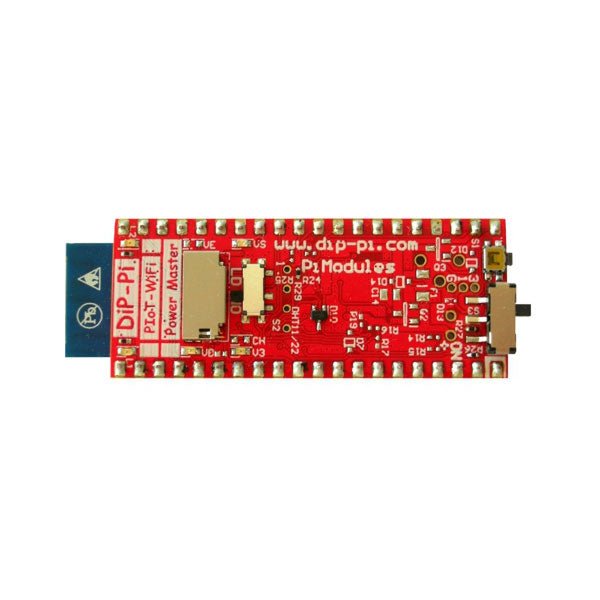

Pi Modules DiP-Pi Pico WiFi Master for Raspberry Pi Pico
The DiP-Pi WiFi Master is an Advanced WiFi connectivity System with sensors embedded interfaces that cover most of possible needs for IoT application based on Raspberry Pi Pico. It is powered directly from the Raspberry Pi Pico VBUS. The DiP-Pi WiFi Master contains Raspberry Pi Pico embedded RESET button as also ON/OFF Slide Switch that is acting on Raspberry Pi Pico Power Sources. The DiP-Pi WiFi Master is equipped with WiFi ESP8266 Clone module with embedded antenna. This feature open a wide range of IoT applications based on it. In Addition to all above features DiP-Pi WiFi Master is equipped with embedded 1-wire, DHT11/22 sensors, and micro–SD Card interfaces. Combination of the extended powering, battery, and sensors interfaces make the DiP-Pi WiFi Master ideal for IoT applications like data logger, plants monitoring, refrigerators monitoring etc. DiP-Pi WiFi Master is supported with plenty of ready to use examples written in Micro Python or C/C++. Specifications General Dimensions 21 x 51 mm Raspberry Pi Pico pinout compatible Independent Informative LEDs (VBUS, VSYS, V3V3) Raspberry Pi Pico RESET Button ON/OFF Slide Switch acting on Raspberry Pi Pico Powering Source Embedded 3.3 V @ 600 mA LDO ESP8266 Clone WiFi Connectivity ESP8266 Firmware Upload Switch Embedded 1-wire Interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Powering Options Raspberry Pi Pico micro-USB (via VBUS) Embedded Peripherals and Interfaces Embedded 1-wire interface Embedded DHT-11/22 Interface Micro SD Card Socket Programmer Interface Standard Raspberry Pi Pico C/C++ Standard Raspberry Pi Pico Micro Python Case Compatibility DiP-Pi Plexi-Cut Case Informative LEDs VB (VUSB) VS (VSYS) V3 (V3V3) System Protection Direct Raspberry Pi Pico Hardware Reset Button PPTC 500 mA @ 18 V fuse on EPR EPR/LDO Over Temperature protection EPR/LDO Over Current protection System Design Designed and Simulated with PDA Analyzer with one of the most advanced CAD/CAM Tools – Altium Designer Industrial Originated PCB Construction 2 ozcopper PCB manufactured for proper high current supply and cooling 6 mils track/6 mils gap technology 2 layers PCB PCB Surface Finishing – Immersion Gold Multi-layer Copper Thermal Pipes for increased System Thermal Response and better passive cooling Downloads Datasheet Manual
€ 19,95€ 7,98
Members identical
-

Elektor Digital EAGLE V6 Getting Started Guide (E-book)
Whether you are an electronics enthusiast or engineering professional, this book provides the reader with an introduction to the use of the CadSoft’s EAGLE PCB design software package. EAGLE is a user-friendly, powerful and affordable software package for the efficient design of printed circuit boards. It offers the same power and functionality to all users, at a smaller cost than its competitors. A free version of EAGLE is available to enthusiasts for their own use. EAGLE can be used on the main computing platforms including: Microsoft Windows (XP, Vista or Windows 7); Linux (based on kernel 2.6 or above) and Apple Mac OS X (Version 10.6 or higher). Any hardware that supports these software platforms will run the EAGLE application. The book is intended for anyone who wants an introduction to the capabilities of EAGLE. The reader may be a novice at PCB design or a professional wanting to learn about EAGLE, with the intention of migrating from another CAD package. This book will quickly allow you to: obtain an overview of the main modules of EAGLE: the schematic editor; layout editor and autorouter in one single interface; learn to use some of the basic commands in the schematic and layout editor modules of EAGLE; apply your knowledge of EAGLE commands to a small project; learn more about some of the advanced concepts of EAGLE and its capabilities; understand how EAGLE relates to the stages of PCB manufacture; create a complete project, from design through to PCB fabrication. The project discussed in the book is a popular, proven design from the engineering team at Elektor. After reading this book while practicing some of the examples, and completing the projects, the reader should feel confident about taking on more challenging endeavors.
€ 29,95
Members € 23,96
-

Evil Mad Science Easel Board for AxiDraw (Tabloid/A3)
Extra easel boards for AxiDraw V3/A3 can be used as replacements, or for staging additional workpieces for quickly swapping to the next plot. This set consists of one 11.75 x 17 inch (29.85 x 43.18 cm) hardboard platen with rubber feet attached, plus eight micro binder clips.
€ 17,95€ 7,18
Members identical
-

Elektor Publishing Electric Guitar (2nd Edition)
Sound Secrets and Technology What would today’s rock and pop music be without electric lead and bass guitars? These instruments have been setting the tone for more than sixty years. Their underlying sound is determined largely by their electrical components. But, how do they actually work? Almost no one is able to explain this to the true musician with no technical background. This book answers many questions simply, in an easily-understandable manner. For the interested musician (and others), this book unveils, in a simple and well-grounded way, what have, until now, been regarded as manufacturer secrets. The examination explores deep within the guitar, including pickups and electrical environment, so that guitar electronics are no longer considered highly secret. With a few deft interventions, many instruments can be rendered more versatile and made to sound a lot better – in the most cost-effective manner. The author is an experienced electronics professional and active musician. He has thoroughly tested everything described here, in practice.
€ 39,95
Members € 35,96
-

Elektor Digital Electric Guitar (2nd Edition) (E-book)
Sound Secrets and Technology What would today’s rock and pop music be without electric lead and bass guitars? These instruments have been setting the tone for more than sixty years. Their underlying sound is determined largely by their electrical components. But, how do they actually work? Almost no one is able to explain this to the true musician with no technical background. This book answers many questions simply, in an easily-understandable manner. For the interested musician (and others), this book unveils, in a simple and well-grounded way, what have, until now, been regarded as manufacturer secrets. The examination explores deep within the guitar, including pickups and electrical environment, so that guitar electronics are no longer considered highly secret. With a few deft interventions, many instruments can be rendered more versatile and made to sound a lot better – in the most cost-effective manner. The author is an experienced electronics professional and active musician. He has thoroughly tested everything described here, in practice.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Elektor Digital Electronic Circuits For All (E-book)
This book contains more than 400 simple electronic circuits which are developed and tested in practice by the authors. The technical solutions presented in the book are intended to stimulate the creative imagination of readers and broaden their area of thought. This should allow readers to look beyond the horizons of possibilities and use ordinary electronic items in a new way. This book includes new and original radio electronic multipurpose circuits. The chapters of the book are devoted to power electronics and measuring equipment and contain numerous original circuits of generators, amplifiers, filters, electronic switches based on thyristors and CMOS switch elements. Wired and wireless systems as well as security and safety systems are presented. Due to the high relevance and increased interest of readers in little-known or not readily available information, the different chapters of this book describe the use of electronic devices in industrial electronics and for research, as well as new instruments and equipment for medical use, gas-discharge and Kirlian photography. A number of technical devices presented in this book are related to research of the mysteries of the earth, nature and human beings by using radio electronic devices. This book will be useful for both radio amateurs and professionals.
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Elektor Digital Electronic Security and Espionage (E-book)
A Handbook on DIY Nowadays, security problems are rarely properly solved or correctly addressed. Electronic security is only part of the chain in making a system secure. Electronic security is usually addressed as network or software security, neglecting other aspects, but the chain is only as strong as its weakest link. This book is about electronic hardware security, with an emphasis on problems that you can solve on a shoestring DIY budget. It deals mostly with secure communications, cryptosystems, and espionage. You will quickly appreciate that you can’t simply buy a trustworthy and reliable cryptosystem off the shelf. You will then realise that this applies equally to individuals, corporations, and governments. If you want to increase your electronic security awareness in a world already overcrowded with networks of microphones and cameras, this is a book for you. Furthermore, if you want to do something DIY by designing and expanding upon simple electronic systems, please continue reading. Some of the devices described are already published as projects in the Elektor magazine. Some are still ideas yet to be worked out. Complexity is the main enemy of security, so we'll try to keep to simple systems. Every chapter will analyse real-life espionage events or at least several hypothetical scenarios that will hopefully spark your imagination. The final goal is to build a security-conscious mindset (or “to get into a head of a spy”) which is necessary to recognise possible threats beforehand, to design a truly secure system. Don’t bother reading if: you think you and your secrets are 100% safe and secure you think somebody else can effectively handle your security you think conspiracy theories only exist in theory – Telefunken’s masterpiece the “FS-5000 Harpoon” was built on one!
€ 32,95
Members € 26,36
-

Elektor Digital Electronics for Space (E-book)
Space, the final frontier, will become more and more popular. The space industry is continually growing and new products and services will be required. Innovation is needed for the development of this industry. Today it is no longer possible to follow all the events in field of space. The space market is growing and activities are increasing, especially the market for small-satellites. This book wants to help close the gap and encourage electronic engineers to enter into the fascinating field of space electronics. One of the main difficulties is finding people with knowledge of space electronics design. Nowadays companies have to invest a lot of time and resources to instruct electronic engineers with no experience of space. Only a brief and basic introduction of this topic is typically achieved at university in space engineering lectures. Professionals with practical experience and the necessary theoretical knowledge are scarce. Companies from the space sector are searching for staff with knowledge of space electronics. This book will bring space closer aspiring to the space electronic hobbyists.
€ 24,95
Members € 19,96
-

Elektor Labs Elektor 'Wordy' LED Christmas Tree
Multilingual DIY Kit (incl. 27 RGB LEDs + Raspberry Pi Pico) Bring some engineering magic to your festive season with the Wordy LED Christmas Tree, a unique DIY electronics kit designed by Elektor. This beautifully engineered 3D Christmas tree combines eleven PCBs, a Raspberry Pi Pico, and 27 addressable RGB LEDs to illuminate Christmas greetings in seven languages: Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish. Unlike ordinary LED trees, each word inside the tree has its own light chamber, creating a refined, softly glowing display without sound or flicker. The LEDs are fully WS2812-compatible and driven via the popular Adafruit NeoPixel library, making custom animations and color effects easy to create. Perfect for makers, tinkerers, and festive electronics fans, this kit offers both an enjoyable build and a striking, conversation-worthy decoration. The Wordy Christmas Tree is your perfect holiday maker project! Features Multilingual greetings (7 languages) milled into the front panel 3D construction from 11 interlocking PCBs Powered by Raspberry Pi Pico 27 individually addressable RGB LEDs (pre-mounted) Smooth fade-in and fade-out animations Fully programmable using the Arduino IDE A 5-V power supply (with micro-USB connector) capable of ≥1 A is recommended for maximum brightness (not included) Dimensions (H x W x D): 130 x 115 x 75 mm Included All required PCBs with LEDs and other SMD parts mounted Raspberry Pi Pico (to be soldered & programmed by the user) 3-way pin header (to be soldered by the user) 3-way pin socket (to be soldered by the user) 4x Self-adhesive dome bumpers Project Page Elektor Labs
€ 59,95€ 49,95
Members identical























